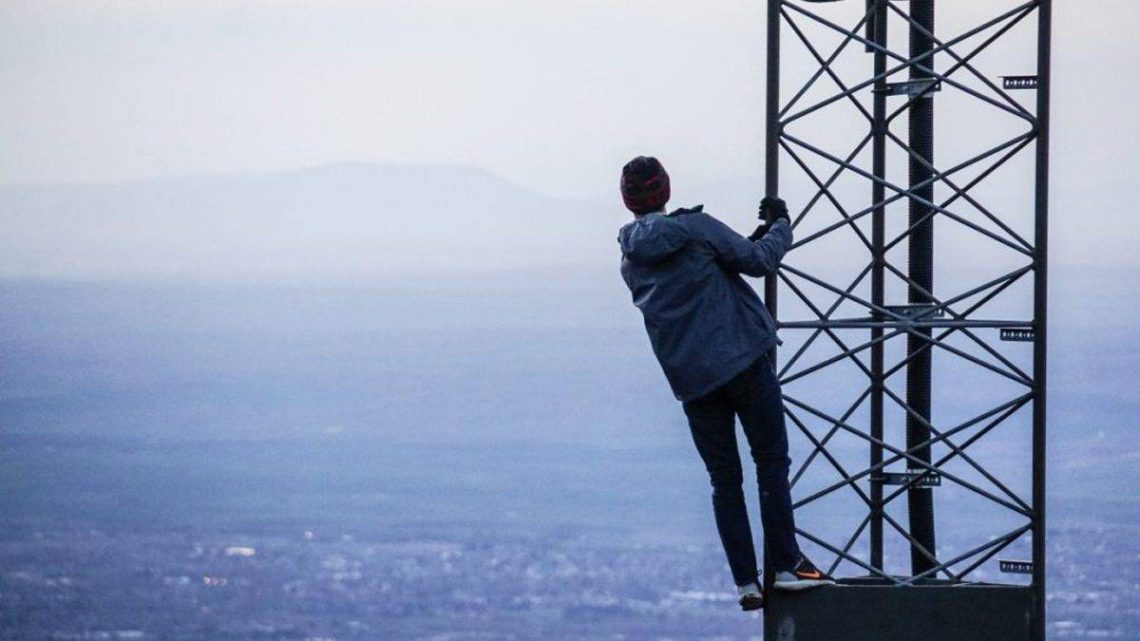
The Thrill Chasers: Unraveling the Concept of Adrenaline Addiction
In the pursuit of adventure and excitement, some individuals find themselves hooked on the electrifying rush that adrenaline provides. The concept of adrenaline addiction, though not officially recognized as a medical condition, captures the essence of those who crave the thrill, seeking out intense experiences to satiate their appetite for excitement. In this blog, we will explore the psychological and physiological aspects of adrenaline addiction, its potential consequences, and ways to strike a balance between thrill-seeking and well-being.
Understanding Adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and neurotransmitter produced by the adrenal glands. It plays a crucial role in the body’s “fight or flight” response to stress. When faced with a perceived threat, adrenaline triggers a cascade of physiological changes, including increased heart rate, heightened alertness, and a surge of energy, preparing the body to confront or escape a danger.
The Thrill-Seeker Mentality
For some individuals, the experience of an adrenaline rush becomes an addictive pursuit. The thrill-seeker mentality is characterized by a constant craving for novel and intense experiences that trigger the release of adrenaline. These individuals may engage in activities such as extreme sports, skydiving, bungee jumping, or other high-risk behaviors to evoke the physiological response associated with adrenaline release.
Psychological Aspects of Adrenaline Addiction
Seeking Intensity: Adrenaline addicts often find themselves drawn to activities that provide an intense, visceral experience. The desire for heightened emotions and sensations becomes a driving force, leading individuals to continuously seek out activities that push their limits.
Risk-Taking Behavior: Engaging in high-risk behavior becomes a way for adrenaline addicts to satisfy their need for excitement. The element of danger adds an extra layer of thrill, contributing to the allure of activities that others might perceive as risky or even reckless.
Novelty and Variety: Adrenaline addicts may struggle with boredom in routine, everyday life. To combat this, they constantly seek novelty and variety, exploring new activities and pushing boundaries to maintain the intensity of their experiences.
Temporary Escapes: The adrenaline rush provides a temporary escape from the stresses and monotony of daily life. For some individuals, the pursuit of excitement becomes a coping mechanism, offering a brief respite from routine and a surge of positive emotions.
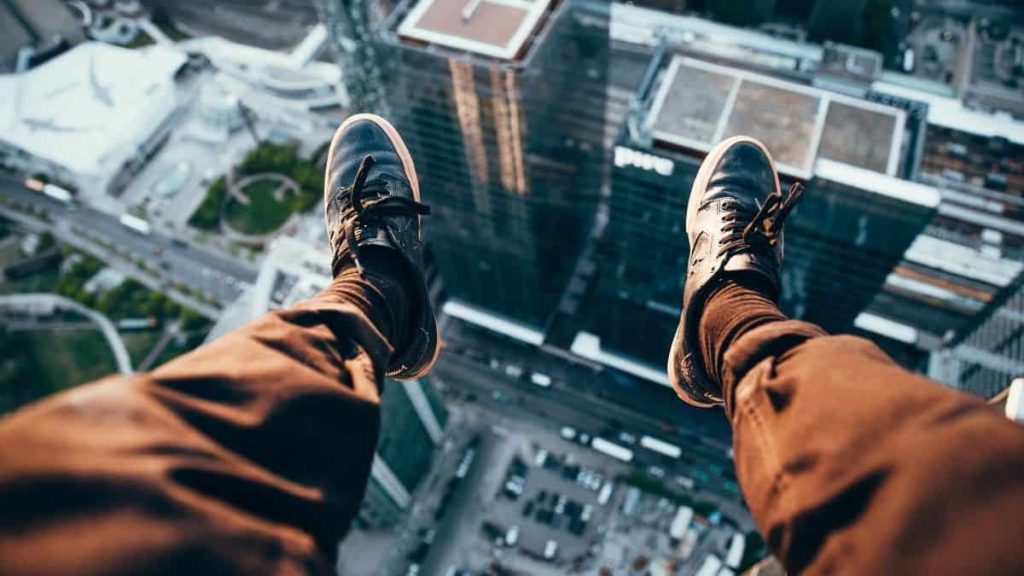

Physiological Aspects of Adrenaline Addiction
Physiological Dependence: Regular exposure to intense adrenaline-inducing activities can lead to a form of physiological dependence. The body may adapt to the elevated levels of adrenaline, requiring more intense stimuli to achieve the same rush over time.
Adrenal Fatigue: Chronic exposure to stress and adrenaline can contribute to adrenal fatigue. This condition occurs when the adrenal glands become overworked, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and disrupted sleep patterns.
Tolerance: Similar to other forms of addiction, individuals may develop a tolerance to adrenaline, requiring increasingly extreme experiences to achieve the same level of excitement. This cycle can perpetuate risky behaviors and lead to a constant escalation of activities.
Consequences of Adrenaline Addiction
Physical Injuries: Engaging in high-risk activities increases the likelihood of physical injuries. Adrenaline addicts may find themselves pushing their bodies to the limit, leading to accidents, fractures, or other injuries.
Mental Health Implications: The constant pursuit of adrenaline can take a toll on mental health. The temporary highs followed by periods of normalcy or even withdrawal can contribute to mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Strained Relationships: Adrenaline addiction may strain relationships, as loved ones may express concern or frustration with the individual’s high-risk behaviors. The constant pursuit of thrill may lead to a disconnect between the adrenaline addict and those who do not share the same enthusiasm for extreme experiences.
Financial Implications: Many adrenaline-inducing activities come with a significant financial cost. The constant need for novel and intense experiences can lead to financial strain as individuals invest in equipment, travel, and participation fees for extreme sports or adventures.
Adrenaline addiction is a complex phenomenon that involves both psychological and physiological components. While seeking excitement and adventure is a natural part of the human experience, it’s essential to strike a balance that prioritizes well-being. Understanding the motivations behind the pursuit of adrenaline, recognizing potential consequences, and exploring healthier alternatives can pave the way for a more sustainable and fulfilling approach to life’s thrills. Ultimately, the goal is to find excitement in a way that enriches life rather than jeopardizes it.
You May Also Like

Real-Life X-Men: Genetic Mutations That Give You ‘Superpowers’
2022-12-28
What is Your Eidetic Memory
2022-04-21


