Unraveling the Aphrodisiac Enigma: Separating Fact from Fiction
The allure of aphrodisiacs has been woven into human culture for centuries, with claims of certain foods, herbs, and substances possessing the power to enhance desire and stimulate passion. From oysters and chocolate to ginseng and exotic herbs, the world is filled with supposed aphrodisiacs. But is there scientific evidence supporting their efficacy, or are these claims rooted in myth and tradition? In this exploration, we delve into the realm of aphrodisiacs to unravel the mystery and discern whether science can substantiate their reputation as passion-inducing agents.
Historical Perspectives on Aphrodisiacs
The history of aphrodisiacs is rich and varied, with cultural beliefs and traditions attributing certain properties to specific foods and substances. Ancient civilizations, including the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians, embraced the concept of aphrodisiacs as a means to enhance fertility, promote love, and elevate the sensual experience. However, historical anecdotes and cultural practices don’t necessarily constitute scientific evidence.
The Psychological Component
A significant aspect of the aphrodisiac phenomenon is the psychological component. The mere belief in the aphrodisiac qualities of a particular food or substance can trigger a placebo effect, leading individuals to perceive increased desire or arousal. The power of suggestion and cultural conditioning can play a significant role in the perceived effectiveness of aphrodisiacs, highlighting the intricate connection between the mind and physical responses.
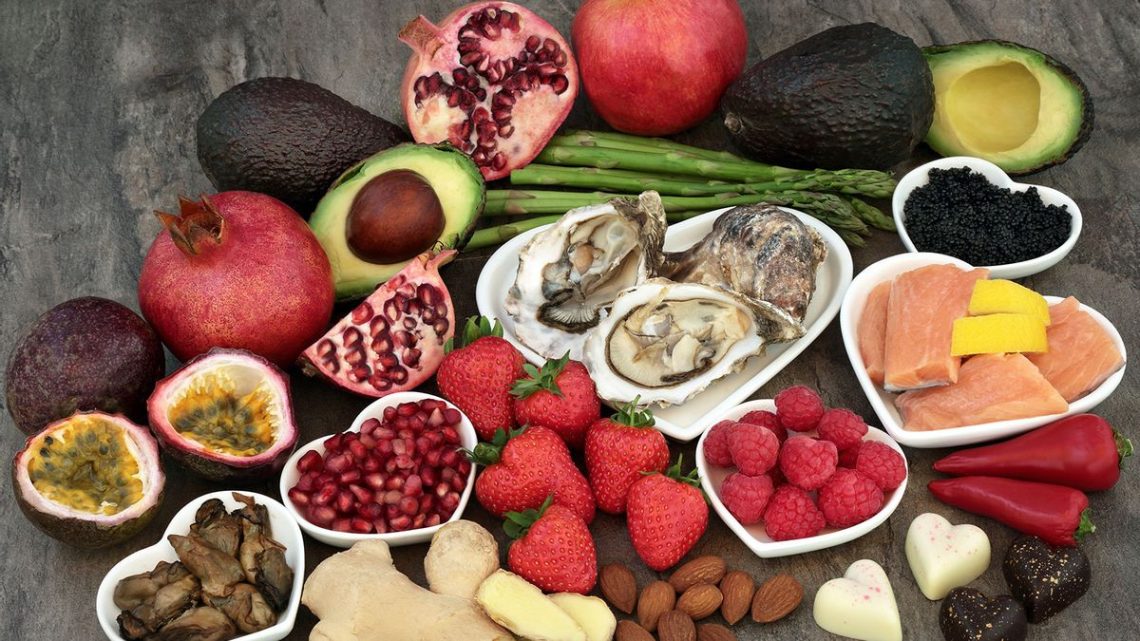
Oysters, Chocolate, and Other Culinary Myths
Oysters and chocolate are often cited as classic aphrodisiacs, with claims of their libido-boosting properties prevalent in popular culture. Oysters contain high levels of zinc, a nutrient linked to testosterone production, but the actual impact on libido is not well-established. Chocolate, on the other hand, contains compounds that may induce feelings of pleasure and euphoria but doesn’t necessarily have a direct influence on sexual desire. Scientifically, these culinary delights may contribute to mood enhancement rather than acting as direct aphrodisiacs.
Herbs and Plants
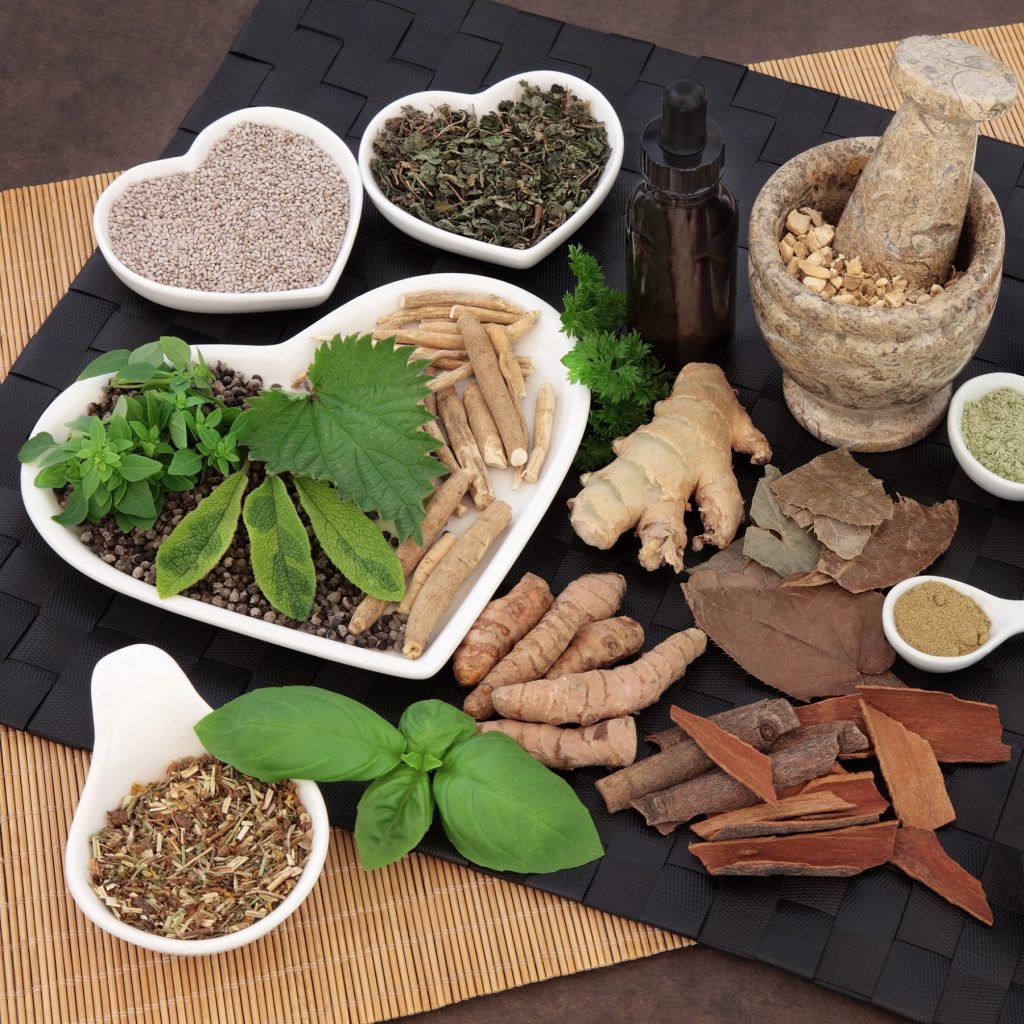
Traditional medicine often incorporates herbs and plants believed to have aphrodisiac properties. Ginseng, maca root, and ginkgo biloba are examples frequently associated with heightened sexual function. While some studies suggest potential benefits for certain herbs in improving aspects of sexual function, the evidence is not conclusive, and more rigorous research is needed to establish causation.

The Role of Chemistry
The science behind aphrodisiacs involves the complex interplay of hormones, neurotransmitters, and physiological responses. Some substances may impact the release of dopamine, serotonin, or other neurotransmitters associated with pleasure and mood regulation. However, the specific mechanisms and the degree to which these substances directly influence sexual desire are often unclear and vary among individuals.
Pharmacological Approaches
In the realm of pharmaceuticals, drugs like Viagra have been developed to address specific issues related to sexual function. While these medications are designed to enhance blood flow and address physiological barriers to arousal, they differ significantly from traditional aphrodisiacs. Unlike the organic nature of foods and herbs, pharmaceuticals are engineered to target specific physiological pathways.
Individual Variation
One of the challenges in studying aphrodisiacs is the considerable variation in individual responses. Factors such as age, health, hormonal balance, and psychological well-being can all influence how a person responds to substances purported to enhance desire. Scientific studies often face difficulty in accounting for these diverse variables, contributing to the complexity of drawing definitive conclusions.
Research Gaps and Methodological Challenges
The scientific investigation of aphrodisiacs faces several challenges. Methodological issues, small sample sizes, and the lack of double-blind, placebo-controlled studies limit the reliability of many existing studies. Additionally, the subjective nature of sexual experiences makes it challenging to measure and quantify the impact of aphrodisiacs consistently.
Potential Aphrodisiacs with Some Scientific Support
While conclusive evidence remains elusive, certain substances have shown promise in scientific studies. For example, saffron has demonstrated potential in improving sexual function in some research. Additionally, the amino acid L-arginine, found in foods like watermelon and nuts, plays a role in nitric oxide production, potentially influencing blood flow.
A Balanced Perspective
In the quest to unravel the mystery of aphrodisiacs, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced perspective. While cultural traditions and personal anecdotes may contribute to the allure of certain foods and substances, scientific evidence often falls short of establishing a direct and unequivocal link between them and enhanced sexual desire. Acknowledging the influence of psychological factors, individual variation, and methodological challenges is key to navigating the landscape of aphrodisiacs with a discerning eye.
In the end, the pursuit of a fulfilling and satisfying sexual life encompasses a spectrum of factors, and embracing a holistic approach that considers physical, emotional, and psychological aspects may offer a more comprehensive and sustainable path to well-being.
You May Also Like

Pulsars: An Account of How Mankind Came Across These Fascinating Phenomena
2021-08-25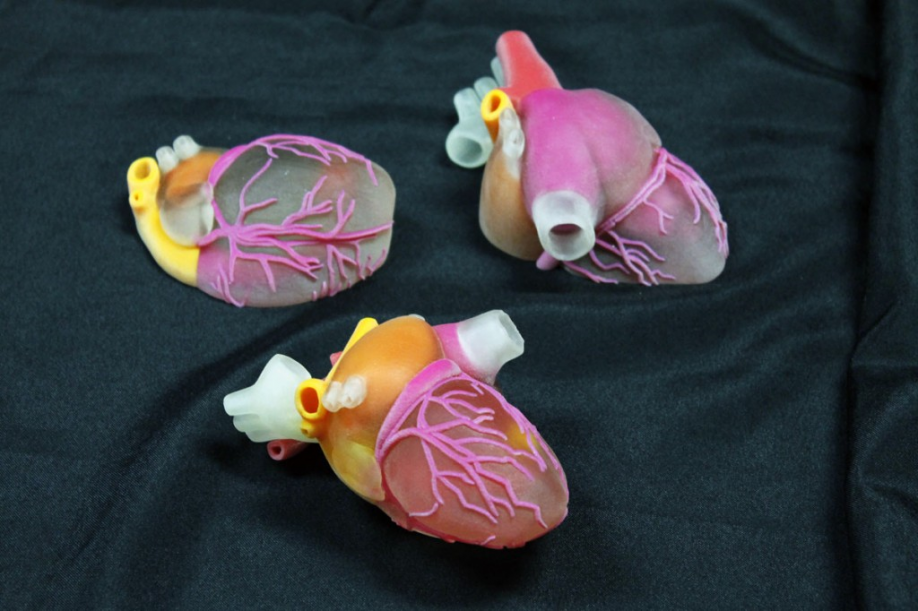
3D Printing and the Medical Industry: Everything You Need to Know
2022-05-25