
Unraveling the Mysteries of Cognition: The Science Behind How We Think
Cognition, often referred to as the “mind’s work,” is the complex and fascinating realm of mental processes that allows us to perceive, think, learn, and remember. From the moment we wake up to the moment we fall asleep, cognition is at play, shaping our understanding of the world. In this blog article, we’ll delve into the science of cognition, exploring its key components, the brain’s role, and how it influences our daily lives.
What Is Cognition?
Cognition encompasses the entire spectrum of mental activities and processes, including perception, memory, problem-solving, language, and decision-making. These processes work together seamlessly to enable us to interact with our surroundings and make sense of the world.
The Key Components of Cognition
Perception: Perception involves the interpretation of sensory information received from our environment. This includes processing visual, auditory, tactile, and olfactory stimuli to create a meaningful understanding of the world around us.
Memory: Memory is the capacity to store, retain, and retrieve information. It plays a critical role in our ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on past experiences.
Language: Language is a fundamental aspect of cognition, allowing us to communicate complex ideas and thoughts. The brain processes language in both receptive (understanding) and expressive (speaking or writing) forms.
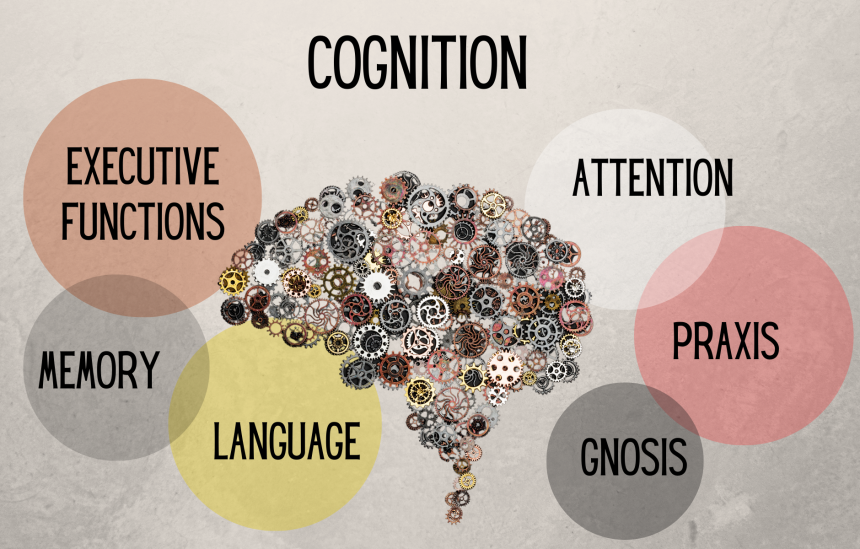
Attention: Attention is the ability to focus on specific information while filtering out irrelevant stimuli. It plays a vital role in tasks requiring concentration and multitasking.
Executive Function: Executive function refers to higher-order cognitive processes responsible for planning, decision-making, problem-solving, and self-control. It helps us manage and organize our thoughts and actions.
Learning: Learning is the process by which we acquire new knowledge or skills through experience. It involves changes in behaviour or understanding as a result of exposure to information.
Emotion: Emotions are intertwined with cognition, influencing our thoughts and decision-making. Emotional intelligence, the ability to recognize and manage emotions, plays a significant role in our social interactions.
The Brain and Cognition
The brain is the central hub of cognition, housing a highly intricate network of neurons that facilitate mental processes. Different regions of the brain are responsible for various aspects of cognition:
Frontal Lobe: The frontal lobe, located at the front of the brain, plays a crucial role in executive functions, decision-making, and problem-solving. It’s also associated with personality and social behaviour.
Temporal Lobe: The temporal lobe, located on the sides of the brain, is involved in language processing, auditory perception, and memory formation.
Parietal Lobe: The parietal lobe processes sensory information and helps us navigate spatial environments. It plays a role in perception, attention, and mathematical reasoning.
Occipital Lobe: Situated at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for visual processing and perception.
Hippocampus: The hippocampus, located deep within the brain, is crucial for the formation of new memories and spatial navigation.
Amygdala: The amygdala, part of the limbic system, is essential for processing emotions and recognizing emotional significance in events.
Prefrontal Cortex: The prefrontal cortex, situated in the frontal lobe, is responsible for higher cognitive functions, including decision-making, planning, and social behaviour.

Cognition in Action
Cognition is not just an abstract concept; it profoundly influences our daily lives. Here’s how cognition plays a role in some common scenarios:
Learning a New Skill: When we embark on learning a new skill, such as playing a musical instrument or speaking a foreign language, cognition is at the forefront. Our brains process information, create associations, and gradually improve our performance through practice and repetition.
Solving Complex Problems: Whether it’s a mathematical puzzle, a challenging work assignment, or a personal dilemma, cognition is what allows us to analyse the problem, generate potential solutions, and select the most appropriate course of action.
Creativity and Innovation: Creative thinking is a product of cognition. When we brainstorm ideas, think outside the box, or create works of art, our cognitive processes are engaged in novel and imaginative ways.
Decision-Making: Every decision we make, from choosing what to wear in the morning to major life decisions, relies on cognitive processes. Our brains weigh options, consider consequences, and ultimately make choices based on our goals, values, and past experiences.
Memory and Nostalgia: Memory is a cornerstone of our identities. It allows us to reminisce about the past, recall cherished memories, and learn from our experiences. Cognitive processes continually shape and reshape our memories.
Language and Communication: The ability to convey thoughts and ideas through language is a testament to the intricacy of cognition. We use language not only for basic communication but also to express complex emotions, share knowledge, and connect with others.
Cognitive Disorders and Challenges
While cognition is a remarkable aspect of human existence, it can be vulnerable to disorders and challenges. Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and depression can significantly impact cognitive function. Understanding these disorders is vital for developing effective treatments and support systems.
The Future of Cognitive Science
Cognitive science is a multidisciplinary field that combines insights from psychology, neuroscience, linguistics, and computer science to advance our understanding of cognition. As technology continues to advance, researchers are using cutting-edge techniques like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and artificial intelligence to delve deeper into the mechanisms of cognition.
You May Also Like
The Ins and Outs of Stem Cell Harvesting
2022-03-04
Omicron; What Do We Know?
2021-12-06


